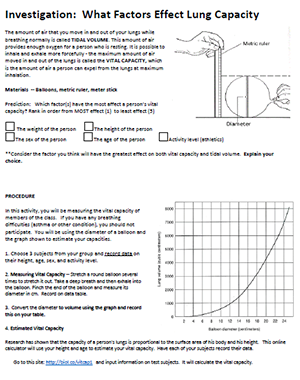
In this investigation, students use balloons and rulers to estimate the vital capacity of lungs using test subjects within the class. To perform the test, subjects take a deep breath and blow into a balloon. The diameter is measured and a graph is used to estimate the volume of air expelled based on the diameter of the balloon.
Students then compare their balloon measurements to the lung capacity measured with a spirometer. Spirometers are medical devices that measure how much air can be inhaled.
Students consider variables such as age, weight, height, sex, and activity level. They collect data to determine which factor has the greatest impact on vital capacity.
In addition to data taken from balloon measurements, students can use a vital capacity calculator online which considers height, sex, and age to determine the approximate lung capacity of the individual.
Though results with such a small sample size are likely to be inconsistent, the calculator reveals that the most important factors are height and sex, which correlates directly with the size of the chest cavity.
Most students will conclude that the larger the person is, the greater their lung capacity.
Grade Level: 9-12
Time Required: 30-45 min
HS-LS1-2 Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms
HS-LS1-3 Plan and conduct an investigation to provide evidence that feedback mechanisms maintain homeostasis.
CCC2: Cause and Effect
CCC6:. Structure and function.

