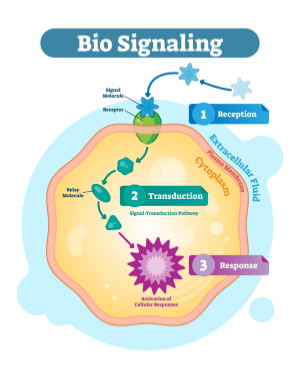
Cell signaling is the process by which cells communicate with each other and respond to external stimuli, ensuring the coordination of vital biological functions. This system involves a signal binding to a receptor on a target cell, and triggering a series of intracellular events.
These signaling pathways often include second messengers, protein kinases, and phosphorylation cascades, ultimately leading to specific cellular responses like gene expression.
Teaching cell signaling in a high school biology class can be both informative and engaging by using a variety of interactive approaches. Start with a simple analogy, such as comparing cell signaling to a text message system, where the signal is the message, the receptor is the recipient’s phone, and the response is the action taken after reading the message.
The Cell Signaling unit can be daunting, since it involves so many enzymes and secondary messengers. You might even cringe when you hear the term “cyclic AMP” and remember that college biology class you nearly failed. (Or is that just me?) Unit 4 of the AP Biology curriculum details what students need to know about cell communication. Here’s how I tackle it.
Lesson Plans for Cell Signaling
1. Slides Presentation – I created these with fill-in boxes for students to write as we go. I find it easier to give them a handout showing multiple signaling pathways than to try to have them write it all out by hand.
Print these for students using a 4 slide layout. Their copies will have blanks for them to fill in concepts as you progress through the slides.
2. Laboratory Investigation – Taste and Signal Transduction with Gymnema Tea
In this lab, students taste samples that are salty, sweet, bitter, and sour. After swishing Gymnema tea in their mouth, their taste receptors are altered. They can no longer taste sweet! The reason is that the tea interferes with the signal transduction pathway.
3. Negative Feedback Loops with Glucagon and Insulin – explores how the pancreas and liver maintain homeostasis by regulating the amount of glucose on the blood
4. Cell Signaling – How Glucose is Taken Up by the Cells – shows a graphic with a glycoprotein receptor and how insulin triggers the transport of Glut-4 to the cell membrane. (Answer key available at TpT)
5. Cell Signaling – Epinephrine – shows a graphic with G proteins, adenylyl cyclase, cAMP, and PKA. Examines how a stimulus triggers the “fight or flight” response.
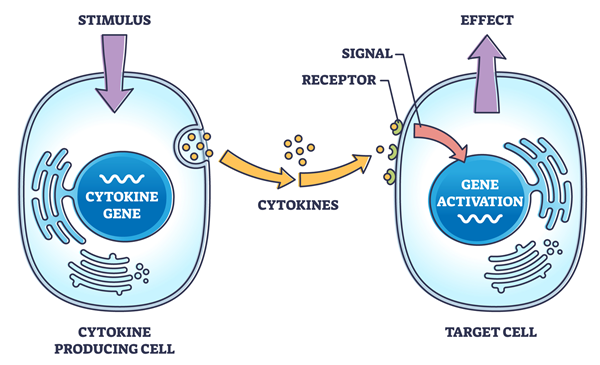
6. Signal Transduction – a final review of the processes showing graphics of signal transductions, phosphorylation cascade, and cytokine signaling. Great for a final review! (Answer key available at TpT)
Related Resources
Complete AP Biology Curriculum with Lesson Links
Quizziz – Practice for the Exam
Video (Khan Academy) – Signal Transduction with explanation on Cholera toxins

