
Biological macromolecules are large, complex molecules essential for life, playing key roles in the structure, function, and regulation of cells. The four main types—carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids—each serve unique and vital purposes. Students in AP Biology will need to know the properties of monomers and the types of bonds that connect them to make polymers.
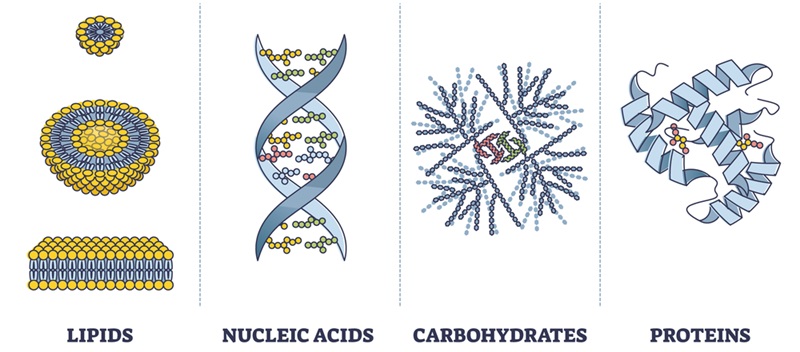
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for living organisms and provide structural support in plants and arthropods. They include simple sugars like glucose as their monomers and larger molecules like starch, glycogen, and cellulose as their polymers.
Lipids are hydrophobic molecules that serve as long-term energy storage, structural components of cell membranes, and signaling molecules. These nonpolar (hydrophobic) molecules include phospholipids, and waxes. Lipids are composed of fatty acids and glycerol.
Proteins, perform a wide variety of functions, including catalyzing chemical reactions, providing structural support, facilitating transport, and defending against pathogens. Made of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, proteins exhibit complex structures that determine their specific roles in the body.
Finally, nucleic acids—DNA and RNA—are the molecules of genetic information. Nucleotides consist of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. DNA stores hereditary information in a double helix structure, while RNA helps translate this information into proteins.
Together, these macromolecules form the foundation of life, and understanding them is critical for students exploring biology. Educational resources on these topics can make learning engaging and accessible, helping students grasp their significance and interconnected roles in living organisms.
Students without a background in chemistry will often struggle with this topic. Dehydration synthesis is the process by which monomers join to form polymers, with the removal of water. Hydrolysis is the process by which a polymer is broken down into monomers.
Resources on Biological Macromolecules
Biomolecules practice – simple worksheet showing monomers, polymers, and chemical formulas (Key, TpT)
Boxing Biomolecules – students create boxes showing each macromolecule with details, can be made into a game
Create a Chart of the Biomolecules – organize information including monomer, examples, function, and sources
Reading Guide (Reinforcement) – using Openstax Biology, chapter 3
Biomolecules: Proteins – use Google slides to learn about proteins, self-paced lesson (Key, Tpt)
Exploring the Chemistry of Adrenaline – students compare adrenaline, pseudoephedrine, and methamphetamine

