Rat Dissection: Structures of the Head and Neck
Rats, like other mammals, have three pairs of major salivary glands along with numerous minor salivary glands scattered throughout the oral cavity. These major salivary glands produce and secrete saliva, which plays important roles in moistening food, initiating the digestive process, and maintaining oral health.
-
Parotid Glands: The parotid glands are the largest of the rat's salivary glands and are located near the ears, beneath the skin. These glands produce a serous (watery) type of saliva that contains enzymes such as amylase, which begins the breakdown of starches in the food.
-
Submandibular Glands: The submandibular glands are located beneath the lower jaw, along the sides of the rat's neck. These glands produce a mixed type of saliva containing both serous and mucous components. The saliva from the submandibular glands helps lubricate food and initiate digestion.
-
Sublingual Glands: The sublingual glands are situated beneath the tongue in the floor of the mouth. They produce a predominantly mucous type of saliva, which is thicker and more viscous than serous saliva. The mucous saliva helps to lubricate the oral cavity and facilitate swallowing.
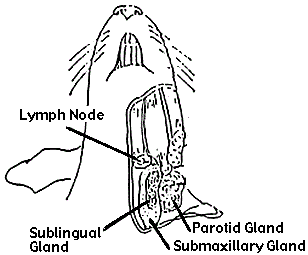
Find the lymph glands which lie anterior to the salivary glands. Lymph glands are dark and circular and are pressed against the jaw muscles
Lymph nodes are small structures that work as filters for foreign substances, such as cancer cells and infections. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid
Beneath the muscles of the neck is the trachea. The trachea is identifiable by its ringed cartilage which provides support. The esophagus lies behind the trachea, but can be difficult to locate in this area.
Locate the larynx, which is just anterior to the trachea. The larynx is the voicebox, and allows rats to make squeaking noises.

Rat Navigation
Step 1: Body Regions
Step 2: External Features
Step 3: Expose the Muscles
Step 4: Expose the Bones
Step 5: Head & Neck
Step 6: Thoracic & Abdomen
Step 7: Urogenital System